This disease is not treatable with current medical technology, but at best, prevention can reduce the chances of getting it. Rabies is highly contagious under certain conditions. Therefore, it should not be ignored. Rabies is an acute infectious disease caused by infection with the rabies virus. It is an infectious disease that can be zoonotic. Humans are mainly infected by the bite of a sick animal.

In recent years, more and more people keep pets in the country, and the mortality rate of rabies morbidity is now known to be the first place in the drama of infectious diseases. The main source of rabies infection in China is the numerous sick dogs, with 80-90% of the transmitters. It is important to note that in recent years there have been several reports of healthy and virus-bearing animals, such as dogs or cats, causing morbidity after scratching and biting people, and these injured animals, still living in good health. Therefore, until you get effective treatment, try not to have too close contact with strange animals for safety.
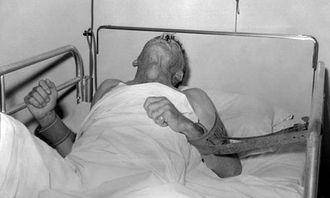
This zoonotic disease occurs mostly in some carnivores such as cats, dogs, and wolves. The incubation period of rabies in humans bitten by diseased animals varies in length, which still depends on the individual’s physical fitness, as well as, the rate of infection of the virus. The majority of cases develop within three months, but the probability of developing rabies within six months is 4-10%, and only 1% of cases develop in more than one year. Typical symptoms of rabies are fear of water, fear of wind, panic, pharyngeal muscle spasms, fear of light, progressive paralysis, irritability, shooting pains and other sensitive symptoms.
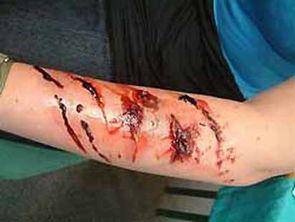
The rabies virus is primarily transmitted through bites, but can also be transmitted through saliva and body fluids with the virus along various scratches, exposed mucous membranes and broken skin. It can also be transmitted through the process of slaughtering and skinning a sick animal. There have been reports from overseas of rabies virus being transmitted from the donor to the recipient as a result of corneal transplantation.
In general, rabid people are not the source of infection and there is no human-to-human transmission.

